Overview – What is DoppelPaymer?
Recently, Proficio’s Threat Intelligence Team has observed a surge in ransomware cases that take advantage of the current COVID-19 situation. In this blog, we will discuss a variant of ransomware named “DoppelPaymer”, which has significantly raised its popularity over the last month, and provide additional details discovered during our research.
Ransomware Details
“DoppelPaymer” is said to be the evolution from “BitPaymer Ransomware”. This strain of ransomware is an enterprise-targeting variant. Based on its history of attacks and the information within the ransom notes, we believe that the threat actor group is targeting English-speaking victims.
While earlier builds of the malware were identified back in April 2019, the first known victims of DoppelPaymer ransomware were seen in June 2019. DoppelPaymer ransomware is likely a variant of BitPaymer Ransomware, where initial ransom notes would contain the string of text “BitPaymer”. The name “DoppelPaymer” was given by researchers to identify this new variant of ransomware found in the wild. Following that, the threat actor appears to have adopted this name and has changed the string of text from “BitPaymer” to “DoppelPaymer” within the ransom notes. Based on the similarities between both ransomware variants, the threat actor groups for DoppelPaymer are suspected to be likely a split from INDRIK SPIDER cybercrime group.
DoppelPaymer Traits
DoppelPaymer ransomware is known to consist of both Dridex and BitPaymer source code. Several other interesting traits that were observed, including:
- Encryption method 2048-bit RSA + 256-bit AES
- Encrypted files are renamed with a “.locked” extension
- Latest version of variants mark data with “.doppeled” appendix
- Ability to terminate processes and services that may interfere with file encryption using the technique ProcessHacker
How does it infect your system?
DoppelPaymer ransomware is usually dropped by the Dridex trojan; however, this ransomware is not limited to one distribution method. Based on our research, the following are some of the distribution methods that have been observed over the year:
- Insecure RDP configuration
- Email spam and malicious attachments
- Deceptive downloads
- Botnets
- Exploits
- Malicious advertisement
- Web injects
- Fake updates
- Repackaged
- Infected installers
Upon successful infection and encryption of data on the victim’s computer, the victim’s files would be renamed, and a ransom note in text file format could be found within the victim’s system.
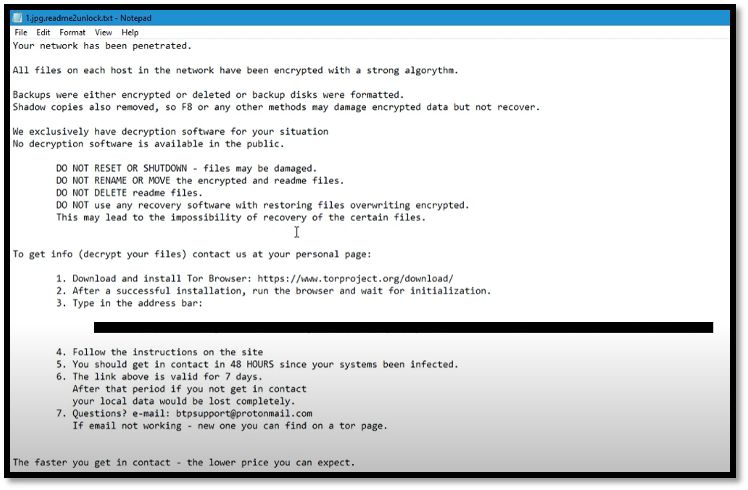
It’s interesting to note that there is no ransom amount stated within the text file. Instead, a list of instructions was being provided to the victim to follow strictly. The victims were requested to download “Tor Browser” and to subsequently type into an address bar provided to access the DoppelPaymer portal.
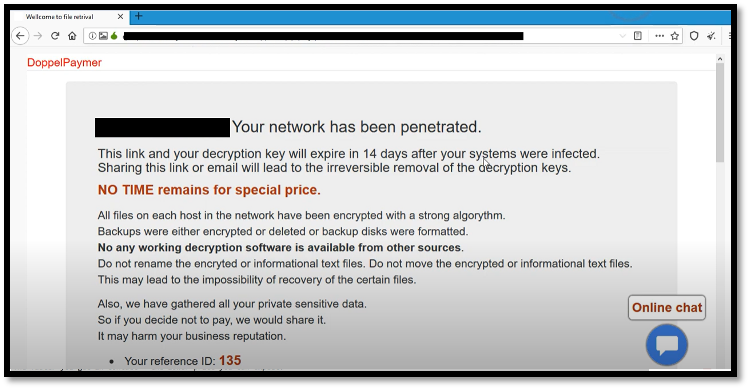
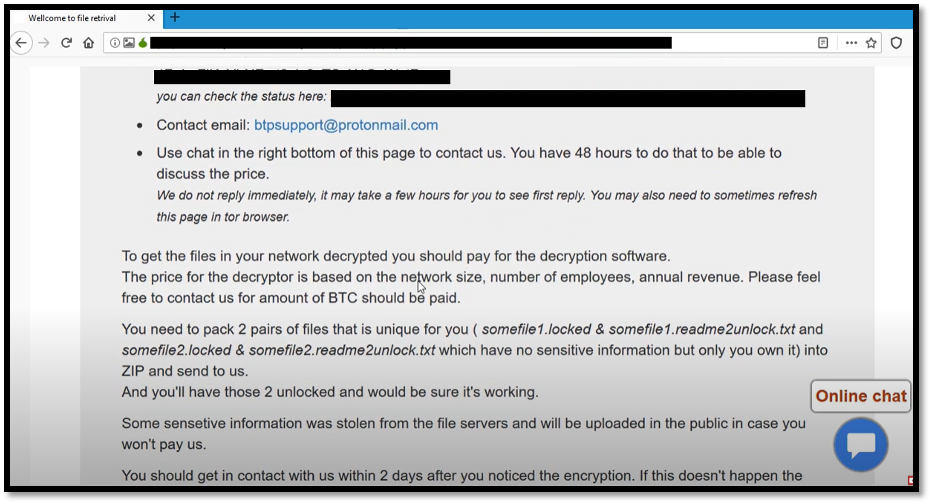
After the portal was accessed from the Tor browser, the victim would be provided with several key pieces of information, such as a countdown timer for a “special price”, a unique reference ID used to identify the victim, the ransom amount and a BTC address where the ransom payment can be sent to.
Further research on DoppelPaymer ransomware reveals that, in the earlier days, victims who are not willing to pay the ransom would have their data sold on the darknet, or dark web. Following the trends from various ransomware groups such as Maze , the DoppelPaymer threat actor group was inspired to launch a public website for use as a shaming platform to victims who are not willing to pay the ransom.
Read our blog article about the resurgence of Raccoon Stealer malware
Precautionary Measures
Prevention is always better than a cure. It is advisable to safeguard yourself and your organization to avoid being the next victim of a ransomware attack. We advise using a managed EDR service to better prepare yourself for dealing with a ransomware attack. We also recommend organizations consider the following measures:
- Keep your anti-virus software / EDR solutions and other security tools installed on the systems updated for detection and prevention from the spread of ransomware.
- Make use of a managed EDR service to quickly react and contain any ransomware vendor
- Managed EDR services can also play a big part in monitoring and alerting on attacked vectors used as a distribution method
- Perform regular backups on critical files and systems.
- Keep your operating systems up to date with the latest security patches.
- Make use of network segmentation alongside the zero-trust model.
- Apply content filters on email gateways and email systems to prevent malicious content from reaching users and reduce the chance of a possible compromise.
- Educate your employees and users to improve cybersecurity awareness.
For the latest information from our Threat Intelligence Team on the DoppelPaymer attacks and other threats, please visit our Twitter Feed or sign up to receive our weekly Proficio Threat Intel newsletter.